 重要提示:
请勿将账号共享给其他人使用,违者账号将被封禁!
重要提示:
请勿将账号共享给其他人使用,违者账号将被封禁!
题目
Fence Co plans to invest in a project which is different to its existing business operations and has identified a company in the same business area as the project, Hex Co. The equity beta of Hex Co is 1·2 and the company has an equity market value of $54 million. The market value of the debt of Hex Co is $12 million.
The risk-free rate of return is 4% per year and the average return on the stock market is 11% per year. Both companies pay corporation tax at a rate of 20% per year.
Required:
(a) Calculate the current weighted average cost of capital of Fence Co. (7 marks)
(b) Calculate a cost of equity which could be used in appraising the new project. (4 marks)
(c) Explain the difference between systematic and unsystematic risk in relation to portfolio theory and the capital asset pricing model. (6 marks)
(d) Discuss the differences between weak form, semi-strong form. and strong form. capital market efficiency, and discuss the significance of the efficient market hypothesis (EMH) for the financial manager. (8 marks)
 更多“The equity beta of Fence Co is 0·9 and the company has issued 10 million ordinary shares.”相关的问题
更多“The equity beta of Fence Co is 0·9 and the company has issued 10 million ordinary shares.”相关的问题
第1题
Beta Blocker Systems is a leading drug research and development facility. In the beginning of 2004, it was widely expected to receive approval to market a new beta blocker that it had developed internally. The new drug has significantly fewer side effects than the competing medications currently on the market.
Beta blockers are widely prescribed for a variety of medical conditions, including hypertension, angina, arrhythmias and congestive heart failure. They are also given to heart attack patients to prevent future heart attacks. Because of the widespread use of beta blockers, the market for them is large and their profitability is enormous.
Analysts put the value of the in-process research and development (R&D) for Beta Blocker Systems’ new drug at a whopping $500 million. The expected approval of the drug, and the consequent benefits to any parent companythat might own it, effectively put Beta Blocker Systems into play as an acquisition candidate.
Alphanumeric Research Laboratories, originally founded by Dr. Alka Klimecki, had grown to become a conglomerate with wide-ranging interests in nanotechnology, computer software, biotech, and other industries heavily reliant on research and development. Because of Alphanumeric’s diverse asset base, it was in a position to outbid other firms for Beta Blocker Systems. Alphanumeric Research Labs won the bidding war with an offer of $4.9 billion in Alphanumeric equity to buy out Beta Blocker shareholders. The transaction closed on June 30, 2004. (All balance sheet figures are calculated as of this date.) Alphanumeric recorded the acquisition as a purchase.
The buyout was a windfall for Beta Blocker Systems shareholders. Although the company had very valuable research facilities (shown on its balance sheet at $500 million below its fair market value), it had only $75 million in cash, not enough to fund the necessary development and marketing of the drug on its own without adversely impacting ongoing operations. It had also mismanaged its inventory, allowing much of it to become obsolete and forcing a write-down to its fair market value of $800 million.
The good news on Beta Blocker’s balance sheet was that it had virtually no debt. Owners’ equity stood at $3.335 billion, with the rest of the liabilities side of the balance sheet captured by a small level of current liabilities. However, this lack of debt seriously diluted the return to equity shareholders. Beta Blocker would have earned $40 million in net income in FY2004 (equally distributed throughout the year) if the acquisition had not taken place, providing a paltry return on owners’ equity.
Alphanumeric Research had an even more remarkable lack of leverage. Current liabilities of only $20 million paled in comparison with Alphanumeric’s stunning $4.530 billion in owners’ equity. Alphanumeric also managed its inventory much better than Beta Blocker Systems had. Its balance sheet showed only $500 million in inventory, all of which was current. In fact, Alphanumeric’s inventory had a fair market value 20 percent higher than book value.
Dr. Klimecki was pleased that the acquisition would further reduce Alphanumeric’s already miniscule total liabilities/owners’ equity ratio because of the additional equity issued to fund the purchase. The auditor, Nancy Alsen, added that the current assets/current liabilities ratio would also improve due to the write-up of inventory to fair market value.
Alphanumeric also had $50 million in cash. The remainder of Alphanumeric Systems’ assets were its research facilities, which had a fair market value of $4.2 billion, much larger than the $3 billion fair market value of Beta Blocker’s facilities.
Both Alphanumeric Research Laboratories and Beta Blocker Systems use fiscal years that match the calendar year and report in accordance with IAS standards. They amortize tangible assets over 20 years, and use the straight-line method for depreciation and amortization of both tangible and intangible assets.
Part 3)
What is the level of equity (in millions) on Alphanumeric’s consolidated balance sheet immediately following the acquisition?
A)$4,530.
B)$4,900.
C)$7,885.
D)$9,430.
第2题
Beta Blocker Systems is a leading drug research and development facility. In the beginning of 2004, it was widely expected to receive approval to market a new beta blocker that it had developed internally. The new drug has significantly fewer side effects than the competing medications currently on the market.
Beta blockers are widely prescribed for a variety of medical conditions, including hypertension, angina, arrhythmias and congestive heart failure. They are also given to heart attack patients to prevent future heart attacks. Because of the widespread use of beta blockers, the market for them is large and their profitability is enormous.
Analysts put the value of the in-process research and development (R&D) for Beta Blocker Systems’ new drug at a whopping $500 million. The expected approval of the drug, and the consequent benefits to any parent companythat might own it, effectively put Beta Blocker Systems into play as an acquisition candidate.
Alphanumeric Research Laboratories, originally founded by Dr. Alka Klimecki, had grown to become a conglomerate with wide-ranging interests in nanotechnology, computer software, biotech, and other industries heavily reliant on research and development. Because of Alphanumeric’s diverse asset base, it was in a position to outbid other firms for Beta Blocker Systems. Alphanumeric Research Labs won the bidding war with an offer of $4.9 billion in Alphanumeric equity to buy out Beta Blocker shareholders. The transaction closed on June 30, 2004. (All balance sheet figures are calculated as of this date.) Alphanumeric recorded the acquisition as a purchase.
The buyout was a windfall for Beta Blocker Systems shareholders. Although the company had very valuable research facilities (shown on its balance sheet at $500 million below its fair market value), it had only $75 million in cash, not enough to fund the necessary development and marketing of the drug on its own without adversely impacting ongoing operations. It had also mismanaged its inventory, allowing much of it to become obsolete and forcing a write-down to its fair market value of $800 million.
The good news on Beta Blocker’s balance sheet was that it had virtually no debt. Owners’ equity stood at $3.335 billion, with the rest of the liabilities side of the balance sheet captured by a small level of current liabilities. However, this lack of debt seriously diluted the return to equity shareholders. Beta Blocker would have earned $40 million in net income in FY2004 (equally distributed throughout the year) if the acquisition had not taken place, providing a paltry return on owners’ equity.
Alphanumeric Research had an even more remarkable lack of leverage. Current liabilities of only $20 million paled in comparison with Alphanumeric’s stunning $4.530 billion in owners’ equity. Alphanumeric also managed its inventory much better than Beta Blocker Systems had. Its balance sheet showed only $500 million in inventory, all of which was current. In fact, Alphanumeric’s inventory had a fair market value 20 percent higher than book value.
Dr. Klimecki was pleased that the acquisition would further reduce Alphanumeric’s already miniscule total liabilities/owners’ equity ratio because of the additional equity issued to fund the purchase. The auditor, Nancy Alsen, added that the current assets/current liabilities ratio would also improve due to the write-up of inventory to fair market value.
Alphanumeric also had $50 million in cash. The remainder of Alphanumeric Systems’ assets were its research facilities, which had a fair market value of $4.2 billion, much larger than the $3 billion fair market value of Beta Blocker’s facilities.
Both Alphanumeric Research Laboratories and Beta Blocker Systems use fiscal years that match the calendar year and report in accordance with IAS standards. They amortize tangible assets over 20 years, and use the straight-line method for depreciation and amortization of both tangible and intangible assets.
Part 5)
Which statement about U.S. GAAP and IAS GAAP is FALSE?
A)The current ratio of the consolidated firm under both accounting standards is typically higher than the pre-acquisition current ratio of either individual firm.
B)Both require capitalization of in-process R&D.
C)Both require write-up of assets to their fair market value.
D)Goodwill is tested annually for impairment under both methods.
第3题
Beta Blocker Systems is a leading drug research and development facility. In the beginning of 2004, it was widely expected to receive approval to market a new beta blocker that it had developed internally. The new drug has significantly fewer side effects than the competing medications currently on the market.
Beta blockers are widely prescribed for a variety of medical conditions, including hypertension, angina, arrhythmias and congestive heart failure. They are also given to heart attack patients to prevent future heart attacks. Because of the widespread use of beta blockers, the market for them is large and their profitability is enormous.
Analysts put the value of the in-process research and development (R&D) for Beta Blocker Systems’ new drug at a whopping $500 million. The expected approval of the drug, and the consequent benefits to any parent companythat might own it, effectively put Beta Blocker Systems into play as an acquisition candidate.
Alphanumeric Research Laboratories, originally founded by Dr. Alka Klimecki, had grown to become a conglomerate with wide-ranging interests in nanotechnology, computer software, biotech, and other industries heavily reliant on research and development. Because of Alphanumeric’s diverse asset base, it was in a position to outbid other firms for Beta Blocker Systems. Alphanumeric Research Labs won the bidding war with an offer of $4.9 billion in Alphanumeric equity to buy out Beta Blocker shareholders. The transaction closed on June 30, 2004. (All balance sheet figures are calculated as of this date.) Alphanumeric recorded the acquisition as a purchase.
The buyout was a windfall for Beta Blocker Systems shareholders. Although the company had very valuable research facilities (shown on its balance sheet at $500 million below its fair market value), it had only $75 million in cash, not enough to fund the necessary development and marketing of the drug on its own without adversely impacting ongoing operations. It had also mismanaged its inventory, allowing much of it to become obsolete and forcing a write-down to its fair market value of $800 million.
The good news on Beta Blocker’s balance sheet was that it had virtually no debt. Owners’ equity stood at $3.335 billion, with the rest of the liabilities side of the balance sheet captured by a small level of current liabilities. However, this lack of debt seriously diluted the return to equity shareholders. Beta Blocker would have earned $40 million in net income in FY2004 (equally distributed throughout the year) if the acquisition had not taken place, providing a paltry return on owners’ equity.
Alphanumeric Research had an even more remarkable lack of leverage. Current liabilities of only $20 million paled in comparison with Alphanumeric’s stunning $4.530 billion in owners’ equity. Alphanumeric also managed its inventory much better than Beta Blocker Systems had. Its balance sheet showed only $500 million in inventory, all of which was current. In fact, Alphanumeric’s inventory had a fair market value 20 percent higher than book value.
Dr. Klimecki was pleased that the acquisition would further reduce Alphanumeric’s already miniscule total liabilities/owners’ equity ratio because of the additional equity issued to fund the purchase. The auditor, Nancy Alsen, added that the current assets/current liabilities ratio would also improve due to the write-up of inventory to fair market value.
Alphanumeric also had $50 million in cash. The remainder of Alphanumeric Systems’ assets were its research facilities, which had a fair market value of $4.2 billion, much larger than the $3 billion fair market value of Beta Blocker’s facilities.
Both Alphanumeric Research Laboratories and Beta Blocker Systems use fiscal years that match the calendar year and report in accordance with IAS standards. They amortize tangible assets over 20 years, and use the straight-line method for depreciation and amortization of both tangible and intangible assets.
Part 6)
Regarding Klimecki’s and Alsen’s statements about the impact of the Beta Systems acquisition on Alphanumeric’s consolidated balance sheet:
A)Klimecki’s statement is correct and Alsen’s statement is incorrect.
B)Klimecki’s statement is correct and Alsen’s statement is correct.
C)Klimecki’s statement is incorrect and Alsen’s statement is incorrect.
D)Klimecki’s statement is incorrect and Alsen’s statement is correct.
第4题
Beta Blocker Systems is a leading drug research and development facility. In the beginning of 2004, it was widely expected to receive approval to market a new beta blocker that it had developed internally. The new drug has significantly fewer side effects than the competing medications currently on the market.
Beta blockers are widely prescribed for a variety of medical conditions, including hypertension, angina, arrhythmias and congestive heart failure. They are also given to heart attack patients to prevent future heart attacks. Because of the widespread use of beta blockers, the market for them is large and their profitability is enormous.
Analysts put the value of the in-process research and development (R&D) for Beta Blocker Systems’ new drug at a whopping $500 million. The expected approval of the drug, and the consequent benefits to any parent companythat might own it, effectively put Beta Blocker Systems into play as an acquisition candidate.
Alphanumeric Research Laboratories, originally founded by Dr. Alka Klimecki, had grown to become a conglomerate with wide-ranging interests in nanotechnology, computer software, biotech, and other industries heavily reliant on research and development. Because of Alphanumeric’s diverse asset base, it was in a position to outbid other firms for Beta Blocker Systems. Alphanumeric Research Labs won the bidding war with an offer of $4.9 billion in Alphanumeric equity to buy out Beta Blocker shareholders. The transaction closed on June 30, 2004. (All balance sheet figures are calculated as of this date.) Alphanumeric recorded the acquisition as a purchase.
The buyout was a windfall for Beta Blocker Systems shareholders. Although the company had very valuable research facilities (shown on its balance sheet at $500 million below its fair market value), it had only $75 million in cash, not enough to fund the necessary development and marketing of the drug on its own without adversely impacting ongoing operations. It had also mismanaged its inventory, allowing much of it to become obsolete and forcing a write-down to its fair market value of $800 million.
The good news on Beta Blocker’s balance sheet was that it had virtually no debt. Owners’ equity stood at $3.335 billion, with the rest of the liabilities side of the balance sheet captured by a small level of current liabilities. However, this lack of debt seriously diluted the return to equity shareholders. Beta Blocker would have earned $40 million in net income in FY2004 (equally distributed throughout the year) if the acquisition had not taken place, providing a paltry return on owners’ equity.
Alphanumeric Research had an even more remarkable lack of leverage. Current liabilities of only $20 million paled in comparison with Alphanumeric’s stunning $4.530 billion in owners’ equity. Alphanumeric also managed its inventory much better than Beta Blocker Systems had. Its balance sheet showed only $500 million in inventory, all of which was current. In fact, Alphanumeric’s inventory had a fair market value 20 percent higher than book value.
Dr. Klimecki was pleased that the acquisition would further reduce Alphanumeric’s already miniscule total liabilities/owners’ equity ratio because of the additional equity issued to fund the purchase. The auditor, Nancy Alsen, added that the current assets/current liabilities ratio would also improve due to the write-up of inventory to fair market value.
Alphanumeric also had $50 million in cash. The remainder of Alphanumeric Systems’ assets were its research facilities, which had a fair market value of $4.2 billion, much larger than the $3 billion fair market value of Beta Blocker’s facilities.
Both Alphanumeric Research Laboratories and Beta Blocker Systems use fiscal years that match the calendar year and report in accordance with IAS standards. They amortize tangible assets over 20 years, and use the straight-line method for depreciation and amortization of both tangible and intangible assets.
Part 1)
What is the amount of goodwill (in millions) that Alphanumeric will record on its June 30, 2004 balance sheet to reflect the acquisition of Beta Blocker Systems?
A)$25.
B)$40.
C)$125.
D)$565.
第5题
Beta Blocker Systems is a leading drug research and development facility. In the beginning of 2004, it was widely expected to receive approval to market a new beta blocker that it had developed internally. The new drug has significantly fewer side effects than the competing medications currently on the market.
Beta blockers are widely prescribed for a variety of medical conditions, including hypertension, angina, arrhythmias and congestive heart failure. They are also given to heart attack patients to prevent future heart attacks. Because of the widespread use of beta blockers, the market for them is large and their profitability is enormous.
Analysts put the value of the in-process research and development (R&D) for Beta Blocker Systems’ new drug at a whopping $500 million. The expected approval of the drug, and the consequent benefits to any parent companythat might own it, effectively put Beta Blocker Systems into play as an acquisition candidate.
Alphanumeric Research Laboratories, originally founded by Dr. Alka Klimecki, had grown to become a conglomerate with wide-ranging interests in nanotechnology, computer software, biotech, and other industries heavily reliant on research and development. Because of Alphanumeric’s diverse asset base, it was in a position to outbid other firms for Beta Blocker Systems. Alphanumeric Research Labs won the bidding war with an offer of $4.9 billion in Alphanumeric equity to buy out Beta Blocker shareholders. The transaction closed on June 30, 2004. (All balance sheet figures are calculated as of this date.) Alphanumeric recorded the acquisition as a purchase.
The buyout was a windfall for Beta Blocker Systems shareholders. Although the company had very valuable research facilities (shown on its balance sheet at $500 million below its fair market value), it had only $75 million in cash, not enough to fund the necessary development and marketing of the drug on its own without adversely impacting ongoing operations. It had also mismanaged its inventory, allowing much of it to become obsolete and forcing a write-down to its fair market value of $800 million.
The good news on Beta Blocker’s balance sheet was that it had virtually no debt. Owners’ equity stood at $3.335 billion, with the rest of the liabilities side of the balance sheet captured by a small level of current liabilities. However, this lack of debt seriously diluted the return to equity shareholders. Beta Blocker would have earned $40 million in net income in FY2004 (equally distributed throughout the year) if the acquisition had not taken place, providing a paltry return on owners’ equity.
Alphanumeric Research had an even more remarkable lack of leverage. Current liabilities of only $20 million paled in comparison with Alphanumeric’s stunning $4.530 billion in owners’ equity. Alphanumeric also managed its inventory much better than Beta Blocker Systems had. Its balance sheet showed only $500 million in inventory, all of which was current. In fact, Alphanumeric’s inventory had a fair market value 20 percent higher than book value.
Dr. Klimecki was pleased that the acquisition would further reduce Alphanumeric’s already miniscule total liabilities/owners’ equity ratio because of the additional equity issued to fund the purchase. The auditor, Nancy Alsen, added that the current assets/current liabilities ratio would also improve due to the write-up of inventory to fair market value.
Alphanumeric also had $50 million in cash. The remainder of Alphanumeric Systems’ assets were its research facilities, which had a fair market value of $4.2 billion, much larger than the $3 billion fair market value of Beta Blocker’s facilities.
Both Alphanumeric Research Laboratories and Beta Blocker Systems use fiscal years that match the calendar year and report in accordance with IAS standards. They amortize tangible assets over 20 years, and use the straight-line method for depreciation and amortization of both tangible and intangible assets.
Part 4)
What is Beta Blockers’ contribution (in millions) to Alphanumeric’s FY04 net income (assuming they are both profitable and face a 40 percent tax rate)?
A)-$70.
B)$40.
C)$20.
D)-$103.90.
第6题
A., using the infinite period dividend discount model (DDM).
· Sales of $1,000,000.
· Earnings of $150,000.
· Total assets of $800,000.
· Equity of $400,000.
· Dividend payout ratio of 60.0%.
· Average shares outstanding of 75,000.
· Real risk free interest rate of 4.0%.
· Expected inflation rate of 3.0%.
· Expected market return of 13.0%.
· Stock Beta at 2.1.
The per share value of FishnChips stock is approximately: (Note: Carry calculations out to at least 3 decimal places.)
B.Unable to calculate stock value because ke
D.$17.91.
E.$26.86.
第7题

NGN has a cost of equity of 12% per year and has maintained a dividend payout ratio of 45% for several years. The current earnings per share of the company is 80c per share and its earnings have grown at an average rate of 4·5% per year in recent years.
The ex div share price of KFP Co is $4·20 per share and it has an equity beta of 1·2. The 7% bonds of the company are trading on an ex interest basis at $94·74 per $100 bond. The price/earnings ratio of KFP Co is eight times.
The directors of KFP Co believe a cash offer for the shares of NGN would have the best chance of success. It has been suggested that a cash offer could be financed by debt.
Required:
(a) Calculate the weighted average cost of capital of KFP Co on a market value weighted basis. (10 marks)
(b) Calculate the total value of the target company, NGN, using the following valuation methods:
(i) Price/earnings ratio method, using the price/earnings ratio of KFP Co; and
(ii) Dividend growth model. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the relationship between capital structure and weighted average cost of capital, and comment on
the suggestion that debt could be used to finance a cash offer for NGN. (9 marks)
第8题
The statement of financial position of BKB Co provides the following information:
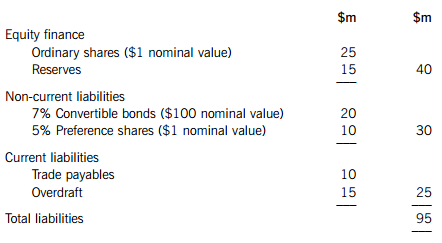
BKB Co has an equity beta of 1·2 and the ex-dividend market value of the company’s equity is $125 million. The ex-interest market value of the convertible bonds is $21 million and the ex-dividend market value of the preference shares is $6·25 million.
The convertible bonds of BKB Co have a conversion ratio of 19 ordinary shares per bond. The conversion date and redemption date are both on the same date in five years’ time. The current ordinary share price of BKB Co is expected to increase by 4% per year for the foreseeable future.
The overdraft has a variable interest rate which is currently 6% per year and BKB Co expects this to increase in the near future. The overdraft has not changed in size over the last financial year, although one year ago the overdraft interest rate was 4% per year. The company’s bank will not allow the overdraft to increase from its current level.
The equity risk premium is 5% per year and the risk-free rate of return is 4% per year. BKB Co pays profit tax at an annual rate of 30% per year.
Required:
(a) Calculate the market value after-tax weighted average cost of capital of BKB Co, explaining clearly any assumptions you make. (12 marks)
(b) Discuss why market value weighted average cost of capital is preferred to book value weighted average cost of capital when making investment decisions. (4 marks)
(c) Comment on the interest rate risk faced by BKB Co and discuss briefly how this risk can be managed. (5 marks)
(d) Discuss the attractions to a company of convertible debt compared to a bank loan of a similar maturity as a source of finance. (4 marks)
第10题
A.分散化投资可实质性地降低报酬率的波动水平,而对报酬率本身却不会同等明显地降低。
B.分散化并不能消除全部风险,有些风险是无法分散掉的,这就是系统性风险。
C.某人持有50家网络公司的股票,可以称他进行了分散化投资。
D.在完美市场中,市场上的风险回报率必定相等
E.beta =1表示无风险资产
F.beta越高要求的风险溢价就越大
 警告:系统检测到您的账号存在安全风险
警告:系统检测到您的账号存在安全风险
为了保护您的账号安全,请在“赏学吧”公众号进行验证,点击“官网服务”-“账号验证”后输入验证码“”完成验证,验证成功后方可继续查看答案!
